optical_io
by Andy Sun (achoenix@gmail.com)
Last update: 2025/10/04
Site Navigation
- Homepage
- Silicon Photonics
- Co-Packaged Optics
- Optical Interposer
- Optical Transceiver
- AI Chip
- System Design
License & Citation
NVIDIA System
Navigation
Comparison Summary
GPU comparison
| Specification | H100 | B100 | B200 | B300 | Rubin | Rubin Ultra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Hopper | Blackwell | Blackwell | Blackwell Ultra | Rubin | Rubin Ultra |
| Process Node | TSMC 4N | TSMC 4NP | TSMC 4NP | TSMC 4NP | Not specified | Not specified |
| Chip Packaging | Monolithic | Dual GB100 dies with NV-HBI | 2 GB100 dies with NV-HBI | 2 GB100 dies with NV-HBI | 2 Rubin dies with NV-HBI | 4 Rubin dies with NV-HBI |
| FP4 Tensor | Not supported | 7 PFLOPS (dense) 14 PFLOPS (sparse) |
10 PFLOPS (dense) 20 PFLOPS (sparse) |
15 PFLOPS (dense) 30 PFLOPS (sparse) |
50 PFLOPS | 100 PFLOPS |
| INT8 Tensor | 0.4 P-OPS | 3.5 P-OPS (dense) 7 P-OPS (sparse) |
5 P-OPS (dense) 9 P-OPS (sparse) |
7.5 P-OPS (dense), 15 P-OPS (sparse) | Not specified | Not specified |
| FP16 Tensor | 0.2 PFLOPS | 1.85 PFLOPS (dense) 3.5 PFLOPS (sparse) |
2.5 PFLOPS (dense) 4.5 PFLOPS (sparse) |
3.75 PFLOPS (dense) 7.5 PFLOPS (sparse) |
Not specified | Not specified |
| FP64 | 34 TFLOPS | 30 TFLOPS | 40 TFLOPS | 68 TFLOPS | Not specified | Not specified |
| Memory | 80 GB HBM3 | 192 GB HBM3e | 192 GB HBM3e | 288 GB HBM3e | 288 GB HBM4 | 1 TB HBM4e |
| Memory Bandwidth | 3.2 TB/s | Up to 8 TB/s (4Tb/s /die) | Up to 8 TB/s (4Tb/s /die) | Up to 8 TB/s (4Tb/s /die) | 8 TB/s /die | 8 TB/s /die |
| Power (TDP) | 700W | 700W | 1,000W | Not specified | Not specified | Not specified |
Note:
- Chip CoWoS Packaging: Each GPU utilizes a dual-die design with two GB100 dies connected via NVIDIA’s NV-High Bandwidth Interface (NV-HBI), providing a 10 TB/s interconnect.
- TDP depends on configurations [tomshardware]
- HGX B200 Configuration: Each B200 GPU is rated at a TDP of 1,000W.
- GB200 Superchip Configuration: When integrated into the GB200 Superchip, a single B200 GPU can have a configurable TDP of up to 1,200W, with the entire superchip (comprising two B200 GPUs and one Grace CPU) reaching up to 2,700W.
- Rubin HBM bandwidth is sourced from: [theregister]
System Comparison
| Specification | H100 NVL8 | Blackwell NVL72 | Blackwell Ultra NVL72 | Rubin NVL144 | Rubin Ultra NVL576 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Trays | N/A | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| GPU | H100 | B100/B200 | B300 | Rubin | Rubin Ultra |
| Number of GPUs | 8 | 72 (144 dies) | 72 (144 dies) | 144 dies | 576 dies |
| CPU | Grace | Grace | Grace | Vera | Vera |
| Number of CPUs | N/A | 18/36 | 36 | 36? | 36? |
| CPU-GPU Bandwidth | TB/s | TB/s | TB/s | 1.8 TB/s | 1.8 TB/s |
| Memory Capacity per GPU | 94 GB HBM3 | 192 GB HBM3e | 288 GB HBM3e | 520 GB HBM4 | 1 TB HBM4e |
| Total Memory Capacity | 752 GB | 13.824 TB | 20.736 TB | 75 TB | 365 TB (inconsistent with 1TB*144) |
| Memory Bandwidth per GPU | 3.9 TB/s | 8 TB/s | 8 TB/s | 13 TB/s | ? TB/s |
| Total Memory Bandwidth | 31.2 TB/s | 576 TB/s | 576 TB/s | ? TB/s | 4500 TB/s |
| Scale-Up Interconnect | NVLink 4 | NVLink 5 | NVLink 5 | NVLink 6 | NVLink 7 |
| Scale-Up Interconnect BW per GPU | 900 GB/s (18x4x100Gb/s) | 1.8 TB/s (18x4x200Gb/s) | 1.8 TB/s | 3.6 TB/s (18x4x400Gb/s?) | ? TB/s (?) |
| Total Scale-Up Bandwidth | 7.2 TB/s | 129.6 TB/s | 129.6 TB/s | 260 TB/s | 1.5 PB/s |
| Server NIC | ConnectX-8 (800Gb/s) | ConnectX-9 (1.6Tb/s) | ConnectX-9 (1.6T/s) | ||
| Scale-Out Interconnect | Not specified | InfiniBand/Ethernet | InfiniBand/Ethernet | InfiniBand/Ethernet | InfiniBand/Ethernet |
| Total Scale-Out Bandwidth | TB/s | TB/s | 14.4 TB/s (144x800Gb/s) | 28.8 TB/s (144x1.6Tb/s) | 115.2 TB/s (576x1.6Tb/s?) |
| Total Rank System Power | 60 kW | 72-120 kW | ? | ? | 600 kW |
| FP4 Dense Inference | PLFOPS | PFLOPS | 1.1 EFLOPS | 3.6 EFLOPS | 15 EFLOPS |
| FP8 Training | PLFOPS | PFLOPS | 0.36 EFLOPS | 1.2 EFLOPS | 5 EFLOPS |
Note:
- System power consumption varies from different sources:
- B200 NVL72 System: Each DGX B200 unit, housing eight B200 GPUs, consumes approximately 14.3 kW. In a standard data center setup, this translates to around 60 kW per rack. [AMAX ENGINEERING]
- GB200 NVL72 System: The GB200 NVL72 rack, comprising 72 GB200 GPUs, has a total power consumption of approximately 120 kW.CONTINUUM LABS
- Since Rubin, the # of GPUs are counted as the # of dies inside a GPU package. This causes confusions for comparison. For example, B300 NVL72 has 72 B300 GPUs with 144 GPU dies (2 dies per GPU packages) while Rubin NVL144 has 144 CPU dies in 72 GPU packages and Rubin Ultra NVL576 has 576 GPU dies in 144 GPU packages.
- Memory bandwidth numbers for Rubin systems shown in GTC 2025 Keynote are not consistent for per GPU and total
- Memory capacity of Rubin Ultra shown in GTC 2025 Keynote are not consistent for per GPU and total
- NVLink 6 bandwidth and ConnextX-9 bandwidth are adopted from source [guru3d]
GB200 NVL72
NVL72 system comes with different designs
| System design | MGX | HGX | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| # of CPU/server | 2 | 1 | |
| # of GPU/server | 4 | 4 | |
| fully connnected HBM within rack | Yes | No |
CPO Switch
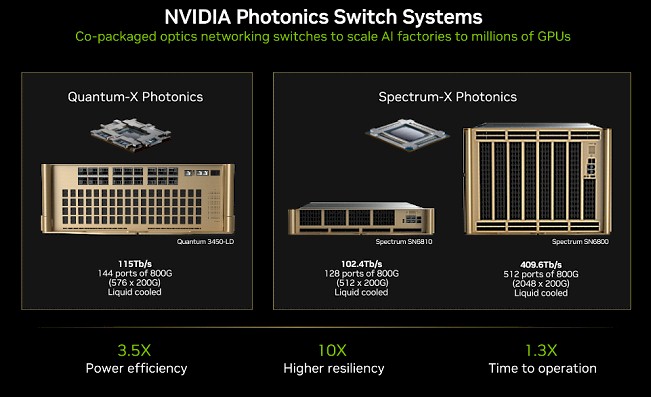
GTC 2025 Keynote
Note
- NVidia will ship Quantum-X (InfiniBand) switch later in 2025, and then a Specturm-X (Ethernet) switch in the second half of 2026.
- Up to 512 fiber ports on the Spectrum-X switch.
- 2 optical transceivers per GPU now, 6 optical transceivers per GPU for larger scale with additional layer of switching
- each transceiver (800G by assumption) costs $1000 and 6W. A 1M GPU datacenter will dedicate 6MW, 10 Rubin Ultra racks for optics
Quantum 3450-LD Switch
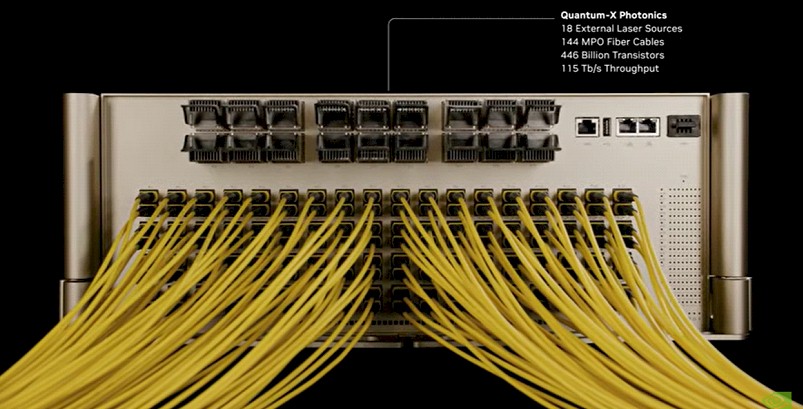

Feature
- 144 ports \@ 800Gb/s, i.e. 115 Tb/s aggregated bandwidth
- 4 Quantum-X CPO switch ASIC (More detailes)
Available in 2025H2
Spectrum SN6810
Feature
- 128 ports \@ 800Gb/s, i.e. 102.4 Tb/s aggregated bandwidth
- 1 Spectrum-X CPO switch ASIC (More detailes)
- extra unused CPO ports may be used for yield-related backup
Spectrum SN6800
Feature
- 512 ports \@ 800Gb/s, i.e. 409.6 Tb/s aggregated bandwidth
- 4 Spectrum-X CPO switch ASIC (More detailes)
- but 6 is needed for non-blocking (2 ASIC to connect the other 4)
Reference
Information
26Q1 Earning Call
- Vera Rubin delivery time
- Huang: 3nm production leadtime >9month
- Note: from wafer-in to CoWoS out. CoWoS may take a month
- Note: meaningful delivery may start 27Q1
- Rubin CPX GDDR7 vs Groq’s SRAM approach
- Huang: CPX runs prefill more efficiently while SRAM is faster than HBM but 1/100 in capacity thus only for certain workload
- Huang: AI workloads vary enormously and need flexibility for TCO